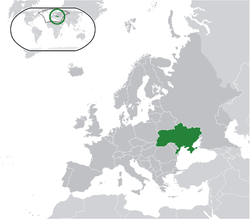

Ukraine (Ukrainian: Україна, transliterated: Ukrayina, [ukrɑˈjinɑ]) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east; Belarus to the north; Poland, Slovakia, and Hungary to the west; Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and Sea of Azov to the south. The city of Kiev (Kyiv) is both the capital and the largest city of Ukraine.
Ukraine's modern history began with the East Slavs. From at least the 9th century, Ukraine was a center of the medieval living area of the East Slavs. This state, known as Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful nation in Europe, but disintegrated in the 12th century. Ukraine was the home of the first modern democracy, which exhibited republican form, during the Khmelnytsky uprising in the 17th century.
After the Great Northern War, Ukraine was divided among a number of regional powers, and by the 19th century, the largest part of Ukraine was integrated into the Russian Empire, with the rest under Austro-Hungarian control. After a chaotic period of incessant warfare and several attempts at independence (1917–21) following World War I and the Russian Civil War, Ukraine emerged in 1922 as one of the founding republics of the Soviet Union. The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic's territory was enlarged westward shortly before and after World War II, and again in 1954 with the Crimea transfer. In 1945, the Ukrainian SSR became one of the co-founding members of the United Nations. Ukraine became independent again after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. This began a period of transition to a market economy, in which Ukraine was stricken with an eight year recession. But since then, the economy has been experiencing a stable increase with GDP growth averaging 24 percent annually.
Ukraine is a unitary state composed of 24 oblasts (provinces), one autonomous republic (Crimea), and two cities with special status: Kiev, its capital, and Sevastopol, which houses the Russian Black Sea Fleet under a leasing agreement. Ukraine is a republic under a semi-presidential system with separate legislative, executive, and judicial branches. Since the collapse of the USSR, Ukraine continues to maintain the second largest military in Europe, after that of Russia. The country is home to 46.2 million people, 77.8 percent of whom are ethnic Ukrainians, with sizable minorities of Russians, Belarusians and Romanians. The Ukrainian language is the only official language in Ukraine, while Russian is also widely spoken. The dominant religion in the country is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which has heavily influenced Ukrainian architecture, literature and music.
Human settlement in the territory of Ukraine dates back to at least 4500 BC, when the Neolithic Cucuteni culture flourished in a wide area that covered parts of modern Ukraine including Trypillia and the entire Dnieper-Dniester region. During the Iron Age, the land was inhabited by Cimmerians, Scythians, and Sarmatians.
Between 700 BC and 200 BC it was part of the Scythian Kingdom, or Scythia. Later, colonies of Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, and the Byzantine Empire, such as Tyras, Olbia, and Hermonassa, were founded, beginning in the 6th century BC, on the northeastern shore of the Black Sea, and thrived well into the 6th century AD. The Goths stayed in the area but came under the sway of the Huns from the 370s AD. In the 7th century AD, the territory of eastern Ukraine was the center of Old Great Bulgaria. At the end of the century, the majority of Bulgar tribes migrated in different directions and the land fell into the Khazars' hands.
Golden Age of Kiev
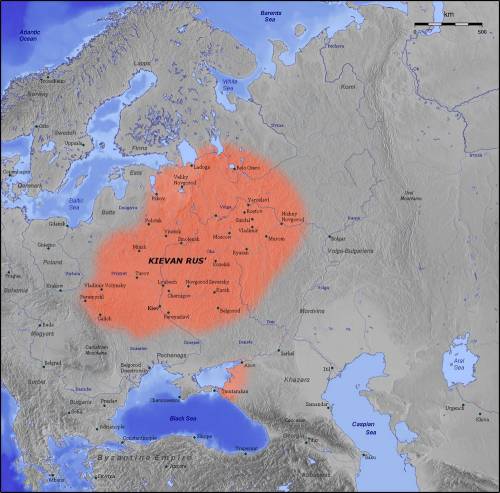
Map of the Kievan Rus' in the 11th century. During the Golden Age of Kiev, the lands of Rus'
covered much of present day Ukraine, Belarus, and western Russia.
In the 9th century, much of modern-day Ukraine was populated by the Rus' people who formed the Kievan Rus'. Kievan Rus' included nearly all territory of modern Ukraine, Belarus, with larger part of it situated on the territory of modern Russia. During the 10th and 11th centuries, it became the largest and most powerful state in Europe.
In the following centuries, it laid the foundation for the national identity of Ukrainians and Russians. Kiev, the capital of modern Ukraine, became the most important city of the Rus'. According to the Primary Chronicle, the Rus' elite initially consisted of Varangians from Scandinavia. The Varangians later became assimilated into the local Slavic population and became part of the Rus' first dynasty, the Rurik Dynasty. Kievan Rus' was composed of several principalities ruled by the interrelated Rurikid Princes. The seat of Kiev, the most prestigious and influential of all principalities, became the subject of many rivalries among Rurikids as the most valuable prize in their quest for power.
The Golden Age of Kievan Rus' began with the reign of Vladimir the Great (980–1015), who turned Rus' toward Byzantine Christianity. During the reign of his son, Yaroslav the Wise (1019–1054), Kievan Rus' reached the zenith of its cultural development and military power. This was followed by the state's increasing fragmentation as the relative importance of regional powers rose again. After a final resurgence under the rule of Vladimir Monomakh (1113–1125) and his son Mstislav (1125–1132), Kievan Rus' finally disintegrated into separate principalities following Mstislav's death.
In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north. The 13th century Mongol invasion devastated Kievan Rus'. Kiev was totally destroyed in 1240. On the Ukrainian territory, the state of Kievan Rus' was succeeded by the principalities of Galich (Halych) and Volodymyr-Volynskyi, which were merged into the state of Galicia-Volhynia.
Foreign domination
By 1569, the Union of Lublin formed the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and a significant part of Ukrainian territory was moved from largely Ruthenized Lithuanian rule to the Polish administration, as it was transferred to the Polish Crown. Under the cultural and political pressure of Polonisation much of the Ruthenian upper class converted to Catholicism and became indistinguishable from the Polish nobility. Thus, the Ukrainian commoners, deprived of their native protectors among Ruthenian nobility, turned for protection to the Cossacks, who remained fiercely orthodox at all times and tended to turn to violence against those they perceived as enemies, particularly the Polish state and its representatives.
The Khanate of Crimea was one of the strongest powers in Eastern Europe until the end of the 17th century.
In the mid-17th century, a Cossack military quasi-state, the Zaporozhian Host, was established by the Dnieper Cossacks and the Ruthenian peasants fleeing Polish serfdom. Poland had little real control of this land, yet they found the Cossacks to be a useful fighting force against the Turks and Tatars, and at times the two allied in military campaigns. However, the continued enserfment of peasantry by the Polish nobility emphasized by the Commonwealth's fierce exploitation of the workforce, and most importantly, the suppression of the Orthodox Church pushed the allegiances of Cossacks away from Poland. Their aspiration was to have representation in Polish Sejm, recognition of Orthodox traditions and the gradual expansion of the Cossack Registry. These were all vehemently denied by the Polish nobility. The Cossacks eventually turned for protection to Orthodox Russia, a decision which would later lead towards the downfall of the Polish-Lithuanian state, and the preservation of the Orthodox Church and in Ukraine.
 In 1648, Bohdan Khmelnytsky led the largest of the Cossack uprisings against the Commonwealth and the Polish king John II Casimir. Left-bank Ukraine was eventually integrated into Russia as the Cossack Hetmanate, following the 1654 Treaty of Pereyaslav and the ensuing Russo-Polish War. After the partitions of Poland at the end of the 18th century by Prussia, Habsburg Austria, and Russia, Western Ukrainian Galicia was taken over by Austria, while the rest of Ukraine was progressively incorporated into the Russian Empire. From the beginning of the 16th century until the end of 17th century the Crimean Tatar raider bands made almost annual forays into agricultural Slavic lands searching for captives to sell as slaves. After the annexation of the Crimean Khanate in 1783, the region was settled by migrants from other parts of Ukraine. Despite the promises of Ukrainian autonomy given by the Treaty of Pereyaslav, the Ukrainian elite and the Cossacks never received the freedoms and the autonomy they were expecting from Imperial Russia. However, within the Empire, Ukrainians rose to the highest offices of Russian state, and the Russian Orthodox Church. At a later period, the tsarist regime carried the policy of Russification of Ukrainian lands, suppressing the use of the Ukrainian language in print, and in public.
In 1648, Bohdan Khmelnytsky led the largest of the Cossack uprisings against the Commonwealth and the Polish king John II Casimir. Left-bank Ukraine was eventually integrated into Russia as the Cossack Hetmanate, following the 1654 Treaty of Pereyaslav and the ensuing Russo-Polish War. After the partitions of Poland at the end of the 18th century by Prussia, Habsburg Austria, and Russia, Western Ukrainian Galicia was taken over by Austria, while the rest of Ukraine was progressively incorporated into the Russian Empire. From the beginning of the 16th century until the end of 17th century the Crimean Tatar raider bands made almost annual forays into agricultural Slavic lands searching for captives to sell as slaves. After the annexation of the Crimean Khanate in 1783, the region was settled by migrants from other parts of Ukraine. Despite the promises of Ukrainian autonomy given by the Treaty of Pereyaslav, the Ukrainian elite and the Cossacks never received the freedoms and the autonomy they were expecting from Imperial Russia. However, within the Empire, Ukrainians rose to the highest offices of Russian state, and the Russian Orthodox Church. At a later period, the tsarist regime carried the policy of Russification of Ukrainian lands, suppressing the use of the Ukrainian language in print, and in public.
World War I and revolution
Ukraine entered World War I on the side of both the Central Powers, under Austria, and the Triple Entente, under Russia. 3.5 million Ukrainians fought with the Imperial Russian Army, while 250,000 fought for the Austro-Hungarian Army. During the war, Austro-Hungarian authorities established the Ukrainian Legion to fight against the Russian Empire. This legion was the foundation of the Ukrainian Galician Army that fought against the Bolsheviks and Poles in the post World War I period (1919–23). Those suspected of the Russophile sentiments in Austria were treated harshly. Up to 5,000 supporters of the Russian Empire from Galicia were detained and placed in Austrian internment camps in Talerhof, Styria, and in a fortress at Terezín (now in the Czech Republic).
With the collapse of the Russian and Austrian empires following World War I and the Russian Revolution of 1917, a Ukrainian national movement for self-determination reemerged. During 1917–20, several separate Ukrainian states briefly emerged: the Ukrainian People's Republic, the Hetmanate, the Directorate and the pro-Bolshevik Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic (or Soviet Ukraine) successively established territories in the former Russian Empire; while the West Ukrainian People's Republic emerged briefly in the former Austro-Hungarian territory. In the midst of Civil War, an anarchist movement called the Black Army led by Nestor Makhno also developed in Southern Ukraine. However with Western Ukraine's defeat in the Polish-Ukrainian War followed by the failure of the further Polish offensive that was repelled by the Bolsheviks. According to the Peace of Riga concluded between the Soviets and Poland, western Ukraine was officially incorporated into Poland who in turn recognised the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic in March 1919, that later became a founding member of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics or the Soviet Union in December, 1922.
Inter-war Soviet Ukraine
The revolution that brought the Soviet government to power devastated Ukraine. It left over 1.5 million people dead and hundreds of thousands homeless. The Soviet Ukraine had to face the famine of 1921. Seeing the exhausted society, the Soviet government remained very flexible during the 1920s. Thus, the Ukrainian culture and language enjoyed a revival, as Ukrainisation became a local implementation of the Soviet-wide Korenisation (literally indigenisation) policy. The Bolsheviks were also committed to introducing universal health care, education and social-security benefits, as well as the right to work and housing. Women's rights were greatly increased through new laws aimed to wipe away centuries-old inequalities. Most of these policies were sharply reversed by the early-1930s after Joseph Stalin gradually consolidated power to become the de facto communist party leader and a dictator of the Soviet Union.
Starting from the late 1920s, Ukraine was involved in the Soviet industrialisation and the republic's industrial output quadrupled in the 1930s. However, the industrialisation had a heavy cost for the peasantry, demographically a backbone of the Ukrainian nation. To satisfy the state's need for increased food supplies and to finance industrialisation, Stalin instituted a program of collectivisation of agriculture as the state combined the peasants' lands and animals into collective farms and enforcing the policies by the regular troops and secret police. Those who resisted were arrested and deported and the increased production quotas were placed on the peasantry. The collectivisation had a devastating effect on agricultural productivity. As the members of the collective farms were not allowed to receive any grain until the unachievable quotas were met, starvation in the Soviet Union became widespread. In 1932–33, millions starved to death in a man-made famine known as Holodomor.

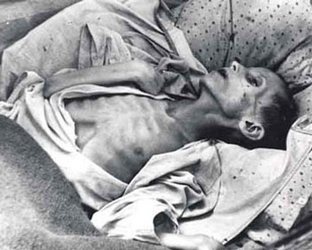
Scholars are divided as to whether this famine fits the definition of genocide, but the Ukrainian parliament and more than a dozen other countries recognise it as such.
The times of industrialisation and Holodomor also coincided with the Soviet assault on the national political and cultural elite often accused in "nationalist deviations". Two waves of Stalinist political repression and persecution in the Soviet Union (1929–34 and 1936–38) resulted in the killing of some 681,692 people; this included four-fifths of the Ukrainian cultural elite and three quarters of all the Red Army's higher-ranking officers.
World War II
 Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, German and Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern Galicia and Volhynia with their Ukrainian population became reunited with the rest of Ukraine. The unification that Ukraine achieved for the first time in its history was a decisive event in the history of the nation.
Following the Invasion of Poland in September 1939, German and Soviet troops divided the territory of Poland. Thus, Eastern Galicia and Volhynia with their Ukrainian population became reunited with the rest of Ukraine. The unification that Ukraine achieved for the first time in its history was a decisive event in the history of the nation.
After France surrendered to Germany, Romania ceded Bessarabia and northern Bukovina to Soviet demands. The Ukrainian SSR incorporated northern and southern districts of Bessarabia, the northern Bukovina, and the Soviet-occupied Hertsa region. But it ceded the western part of the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic to the newly created Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic. All these territorial gains were internationally recognised by the Paris peace treaties of 1947.
German armies invaded the Soviet Union on June 22, 1941, thereby initiating four straight years of incessant total war. The Axis allies initially advanced against desperate but unsuccessful efforts of the Red Army. In the encirclement battle of Kiev, the city was acclaimed as a "Hero City", for the fierce resistance by the Red Army and by the local population. More than 600,000 Soviet soldiers (or one quarter of the Western Front) were killed or taken captive there.
 Although the wide majority of Ukrainians fought alongside the Red Army and Soviet resistance, some elements of the Ukrainian nationalist underground created an anti-Soviet nationalist formation in Galicia, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (1942) that at times engaged the Nazi forces and continued to fight the USSR in the years after the war. Using guerilla war tactics, the insurgents targeted for assassination and terror those who they perceived as representing, or cooperating at any level with, the Soviet state. In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians that fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million to 7 million. The pro-Soviet partisan guerilla resistance in Ukraine is estimated to number at 47,800 from the start of occupation to 500,000 at its peak in 1944; with about 50 percent of them being ethnic Ukrainians. Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are very undependable, ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as much as 100,000 fighters.
Although the wide majority of Ukrainians fought alongside the Red Army and Soviet resistance, some elements of the Ukrainian nationalist underground created an anti-Soviet nationalist formation in Galicia, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (1942) that at times engaged the Nazi forces and continued to fight the USSR in the years after the war. Using guerilla war tactics, the insurgents targeted for assassination and terror those who they perceived as representing, or cooperating at any level with, the Soviet state. In total, the number of ethnic Ukrainians that fought in the ranks of the Soviet Army is estimated from 4.5 million to 7 million. The pro-Soviet partisan guerilla resistance in Ukraine is estimated to number at 47,800 from the start of occupation to 500,000 at its peak in 1944; with about 50 percent of them being ethnic Ukrainians. Generally, the Ukrainian Insurgent Army's figures are very undependable, ranging anywhere from 15,000 to as much as 100,000 fighters.
Initially, the Germans were even received as liberators by some western Ukrainians, who had only joined the Soviet Union in 1939. However, brutal German rule in the occupied territories eventually turned its supporters against the occupation. Nazi administrators of conquered Soviet territories made little attempt to exploit the population of Ukrainian territories' dissatisfaction with Stalinist political and economic policies. Instead, the Nazis preserved the collective-farm system, systematically carried out genocidal policies against Jews, deported others to work in Germany, and began a systematic depopulation of Ukraine to prepare it for German colonisation, which included a food blockade on Kiev.
The vast majority of the fighting in World War II took place on the Eastern Front, and Nazi Germany suffered 93 percent of all casualties there. The total losses inflicted upon the Ukrainian population during the war are estimated between five and eight million, including over half a million Jews killed by the Einsatzgruppen, sometimes with the help of local collaborators. Of the estimated 8.7 million Soviet troops who fell in battle against the Nazis, 1.4 million were ethnic Ukrainians. So to this day, Victory Day is celebrated as one of ten Ukrainian national holidays.
Post-World War II
The republic was heavily damaged by the war, and it required significant efforts to recover. More than 700 cities and towns and 28,000 villages were destroyed. The situation was worsened by a famine in 1946–47 caused by the drought and the infrastructure breakdown that took away tens of thousands of lives.
In 1945 Ukraine was one of the founding members of the United Nations organization. First Soviet computer MESM was built in Kiev Institute of Electrotechnology and became operational in 1950.
According to statistics, as of 1 January 1953, Ukrainians were second only to Russians among adult "special deportees", comprising 20% of the total. Apart from Ukrainians, over 450,000 ethnic Germans from Ukraine and more than 200,000 Crimean Tatars were victims of forced deportations.
Following the death of Stalin in 1953, Nikita Khrushchev became the new leader of the USSR. Being the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Ukrainian SSR in 1938-49, Khrushchev was intimately familiar with the republic and after taking power union-wide, he began to emphasize the friendship between the Ukrainian and Russian nations. In 1954, the 300th anniversary of the Treaty of Pereyaslav was widely celebrated, and in particular, Crimea was transferred from the Russian SFSR to the Ukrainian SSR.
Already by 1950, the republic fully surpassed pre-war levels of industry and production. During the 1946-1950 five year plan nearly 20 percent of the Soviet budget was invested in Soviet Ukraine, a five percent increase from pre-war plans. As a result the Ukrainian workforce rose 33.2 percent from 1940 to 1955 while industrial output grew 2.2 times in that same period. Soviet Ukraine soon became a European leader in industrial production. It also became an important center of the Soviet arms industry and high-tech research. Such an important role resulted in a major influence of the local elite. Many members of the Soviet leadership came from Ukraine, most notably Leonid Brezhnev, who would later oust Khrushchev and become the Soviet leader from 1964 to 1982, as well as many prominent Soviet sportspeople, scientists and artists. On April 26, 1986, a reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant exploded, resulting in the Chernobyl disaster, the worst nuclear reactor accident in history. At the time of the accident seven million people lived in the contaminated territories, including 2.2 million in Ukraine. After the accident, a new city, Slavutych, was built outside the exclusion zone to house and support the employees of the plant which was decommissioned in 2000. A report prepared by the International Atomic Energy Agency and World Health Organization attributed 56 direct deaths to the accident and estimated that there may have been 4,000 extra cancer deaths.
Independence
 On July 16, 1990, the new parliament adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine. The declaration established the principles of the self-determination of the Ukrainian nation, its democracy, political and economic independence, and the priority of Ukrainian law on the Ukrainian territory over Soviet law. A month earlier, a similar declaration was adopted by the parliament of the Russian SFSR. This started a period of confrontation between the central Soviet, and new republican authorities. In August 1991, a conservative faction among the Communist leaders of the Soviet Union attempted a coup to remove Mikhail Gorbachev and to restore the Communist party's power. After the attempt failed, on August 24, 1991 the Ukrainian parliament adopted the Act of Independence in which the parliament declared Ukraine as an independent democratic state. A referendum and the first presidential elections took place on December 1, 1991. That day, more than 90 percent of the Ukrainian people expressed their support for the Act of Independence, and they elected the chairman of the parliament, Leonid Kravchuk to serve as the first President of the country. At the meeting in Brest, Belarus on December 8, followed by Alma Ata meeting on December 21, the leaders of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine, formally dissolved the Soviet Union and formed the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS).
On July 16, 1990, the new parliament adopted the Declaration of State Sovereignty of Ukraine. The declaration established the principles of the self-determination of the Ukrainian nation, its democracy, political and economic independence, and the priority of Ukrainian law on the Ukrainian territory over Soviet law. A month earlier, a similar declaration was adopted by the parliament of the Russian SFSR. This started a period of confrontation between the central Soviet, and new republican authorities. In August 1991, a conservative faction among the Communist leaders of the Soviet Union attempted a coup to remove Mikhail Gorbachev and to restore the Communist party's power. After the attempt failed, on August 24, 1991 the Ukrainian parliament adopted the Act of Independence in which the parliament declared Ukraine as an independent democratic state. A referendum and the first presidential elections took place on December 1, 1991. That day, more than 90 percent of the Ukrainian people expressed their support for the Act of Independence, and they elected the chairman of the parliament, Leonid Kravchuk to serve as the first President of the country. At the meeting in Brest, Belarus on December 8, followed by Alma Ata meeting on December 21, the leaders of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine, formally dissolved the Soviet Union and formed the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Ukraine was initially viewed as a republic with favourable economic conditions in comparison to the other regions of the Soviet Union. However, the country experienced deeper economic slowdown than some of the other former Soviet Republics. During the recession, Ukraine lost 60 percent of its GDP from 1991 to 1999, and suffered five-digit inflation rates. Dissatisfied with the economic conditions, as well as crime and corruption, Ukrainians protested and organised strikes.
The Ukrainian economy stabilized by the end of the 1990s. A new currency, the hryvnia, was introduced in 1996. Since 2000, the country has enjoyed steady real economic growth averaging about seven percent annually. A new Constitution of Ukraine was adopted in 1996, which turned Ukraine into a semi-presidential republic and established a stable political system. Kuchma was, however, criticized by opponents for concentrating too much of power in his office, corruption, transferring public property into hands of loyal oligarchs, discouraging free speech, and electoral fraud.
In 2004, Viktor Yanukovych, then Prime Minister, was declared the winner of the presidential elections, which had been largely rigged, as the Supreme Court of Ukraine later ruled. The results caused a public outcry in support of the opposition candidate, Viktor Yushchenko, who challenged the results and led the peaceful Orange Revolution.
Government and politics
 Ukraine is a republic under a mixed semi-parliamentary semi-presidential system with separate legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The President is elected by popular vote for a five-year term and is the formal head of state.
Ukraine is a republic under a mixed semi-parliamentary semi-presidential system with separate legislative, executive, and judicial branches. The President is elected by popular vote for a five-year term and is the formal head of state.
Ukraine's legislative branch includes the 450-seat unicameral parliament, the Verkhovna Rada. The parliament is primarily responsible for the formation of the executive branch and the Cabinet of Ministers, which is headed by the Prime Minister.
Laws, acts of the parliament and the cabinet, presidential decrees, and acts of the Crimean parliament may be abrogated by the Constitutional Court, should they be found to violate the Constitution of Ukraine. Other normative acts are subject to judicial review. The Supreme Court is the main body in the system of courts of general jurisdiction. Local self-government is officially guaranteed. Local councils and city mayors are popularly elected and exercise control over local budgets. The heads of regional and district administrations are appointed by the president.
Ukraine has a large number of political parties, many of which have tiny memberships and are unknown to the general public. Small parties often join in multi-party coalitions (electoral blocs) for the purpose of participating in parliamentary elections.
Administrative divisions
The system of Ukrainian subdivisions reflects the country's status as a unitary state (as stated in the country's constitution) with unified legal and administrative regimes for each unit.
Ukraine is subdivided into twenty-four oblasts (provinces) and one autonomous republic (avtonomna respublika), Crimea. Additionally, the cities of Kiev, the capital, and Sevastopol, both have a special legal status. The 24 oblasts and Crimea are subdivided into 490 raions (districts), or second-level administrative units. The average area of a Ukrainian raion is 1,200 square kilometres (460 sq mi); the average population of a raion is 52,000 people.
Urban areas (cities) can either be subordinated to the state (as in the case of Kiev and Sevastopol), the oblast or raion administrations, depending on their population and socio-economic importance. Lower administrative units include urban-type settlements, which are similar to rural communities, but are more urbanized, including industrial enterprises, educational facilities, and transport connections, and villages.
In total, Ukraine has 457 cities, 176 of them are labeled oblast-class, 279 smaller raion-class cities, and two special legal status cities. These are followed by 886 urban-type settlements and 28,552 villages.
Geography
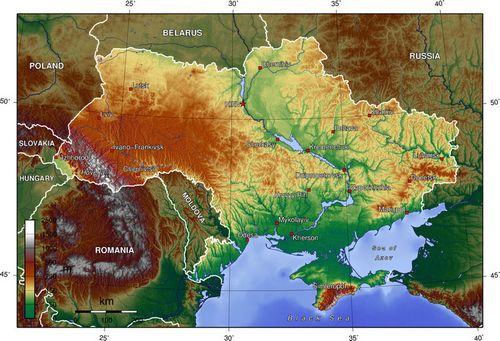
At 603,700 square kilometres (233,100 sq mi) and with a coastline of 2,782 square kilometres (1,074 sq mi), Ukraine is the world's 44th-largest country (after the Central African Republic, before Madagascar). It is the largest whole-Europe country and the second largest country in Europe (after the European part of Russia, before metropolitan France).
The Ukrainian landscape consists mostly of fertile plains (or steppes) and plateaus, crossed by rivers such as the Dnieper (Dnipro), Seversky Donets, Dniester and the Southern Buh as they flow south into the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. To the South-West, the delta of the Danube forms the border with Romania. The country's only mountains are the Carpathian Mountains in the west, of which the highest is the Hora Hoverla at 2,061 metres (6,760 ft), and those on the Crimean peninsula, in the extreme south along the coast.
Ukraine has a mostly temperate continental climate, although a more Mediterranean climate is found on the southern Crimean coast. Precipitation is disproportionately distributed; it is highest in the west and north and lowest in the east and South-East. Western Ukraine, receives around 1,200 millimetres (47 in) of precipitation annually, while Crimea receives around 400 millimetres (16 in). Winters vary from cool along the Black Sea to cold farther inland. Average annual temperatures range from 5.5–7 °C (42–45 °F) in the north, to 11–13 °C (52–55.4 °F) in the south.
Culture
 Ukrainian customs are heavily influenced by Christianity, which is the dominant religion in the country. Gender roles also tend to be more traditional, and grandparents play a greater role in raising children than in the West. The culture of Ukraine has been also influenced by its eastern and western neighbours, which is reflected in its architecture, music and art.
Ukrainian customs are heavily influenced by Christianity, which is the dominant religion in the country. Gender roles also tend to be more traditional, and grandparents play a greater role in raising children than in the West. The culture of Ukraine has been also influenced by its eastern and western neighbours, which is reflected in its architecture, music and art.
The Communist era had quite a strong effect on the art and writing of Ukraine. In 1932, Stalin made socialist realism state policy in the Soviet Union when he promulgated the decree "On the Reconstruction of Literary and Art Organisations". This greatly stifled creativity. During the 1980s glasnost (openness) was introduced and Soviet artists and writers again became free to express themselves as they wanted.
The tradition of the Easter egg, known as pysanky, has long roots in Ukraine. These eggs were drawn on with wax to create a pattern; then, the dye was applied to give the eggs their pleasant colours, the dye did not affect the previously wax-coated parts of the egg. After the entire egg was dyed, the wax was removed leaving only the colourful pattern. This tradition is thousands of years old, and precedes the arrival of Christianity to Ukraine. In the city of Kolomya near the foothills of the Carpathian mountains in 2000 was built the museum of Pysanka which won a nomination as the monument of modern Ukraine in 2007, part of the Seven Wonders of Ukraine action.
The traditional Ukrainian diet includes chicken, pork, beef, fish and mushrooms. Ukrainians also tend to eat a lot of potatoes, grains, fresh and pickled vegetables. Popular traditional dishes include varenyky (boiled dumplings with mushrooms, potatoes, sauerkraut, cottage cheese or cherries), borscht (soup made of beets, cabbage and mushrooms or meat) and holubtsy (stuffed cabbage rolls filled with rice, carrots and meat). Ukrainian specialties also include Chicken Kiev and Kiev Cake. Ukrainians drink stewed fruit, juices, milk, buttermilk (they make cottage cheese from this), mineral water, tea and coffee, beer, wine and horilka.
Literature
 The history of Ukrainian literature dates back to the 11th century, following the Christianisation of the Kievan Rus’. The writings of the time were mainly liturgical and were written in Old Church Slavonic. Historical accounts of the time were referred to as chronicles, the most significant of which was the Primary Chronicle. Literary activity faced a sudden decline during the Mongol invasion of Rus'.
The history of Ukrainian literature dates back to the 11th century, following the Christianisation of the Kievan Rus’. The writings of the time were mainly liturgical and were written in Old Church Slavonic. Historical accounts of the time were referred to as chronicles, the most significant of which was the Primary Chronicle. Literary activity faced a sudden decline during the Mongol invasion of Rus'.
Ukrainian literature again began to develop in the 14th century, and was advanced significantly in the 16th century with the introduction of print and with the beginning of the Cossack era, under both Russian and Polish dominance. The Cossacks established an independent society and popularized a new kind of epic poems, which marked a high point of Ukrainian oral literature. These advances were then set back in the 17th and early 18th centuries, when publishing in the Ukrainian language was outlawed and prohibited. Nonetheless, by the late 18th century modern literary Ukrainian finally emerged.
The 19th century initiated a vernacular period in Ukraine, lead by Ivan Kotliarevsky’s work Eneyida, the first publication written in modern Ukrainian. By the 1830s, Ukrainian romanticism began to develop, and the nation’s most renowned cultural figure, romanticist poet-painter Taras Shevchenko emerged. Where Ivan Kotliarevsky is considered to be the father of literature in the Ukrainian vernacular; Shevchenko is the father of a national revival. Then, in 1863, use of the Ukrainian language in print was effectively prohibited by the Russian Empire. This severely curtained literary activity in the area, and Ukrainian writers were forced to either publish their works in Russian or release them in Austrian controlled Galicia. The ban was never officially lifted, but it became obsolete after the revolution and the Bolsheviks’ coming to power.
Ukrainian literature continued to flourish in the early Soviet years, when nearly all literary trends were approved. These policies faced a steep decline in the 1930s, when Stalin implemented his policy of socialist realism. The doctrine did not necessarily repress the Ukrainian language, but it required writers to follow a certain style in their works. Literary activities continued to be somewhat limited under the communist party, and it was not until Ukraine gained its independence in 1991 when writers were free the express themselves as they wished.
Religion
 The dominant religion in Ukraine is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which is currently split between three Church bodies: the Ukrainian Orthodox Church - Kiev Patriarchate, the Ukrainian Orthodox Church autonomous church body under the Patriarch of Moscow, and the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Church.
The dominant religion in Ukraine is Eastern Orthodox Christianity, which is currently split between three Church bodies: the Ukrainian Orthodox Church - Kiev Patriarchate, the Ukrainian Orthodox Church autonomous church body under the Patriarch of Moscow, and the Ukrainian Autocephalous Orthodox Church.
A distant second by the number of the followers is the Eastern Rite Ukrainian Greek Catholic Church, which practices a similar liturgical and spiritual tradition as Eastern Orthodoxy, but is in communion with the Holy See of the Roman Catholic Church and recognises the primacy of the Pope as head of the Church.
Additionally, there are 863 Roman Catholic communities, and 474 clergy members serving some one million Roman Catholics in Ukraine. The group forms some 2.19 percent of the population and consists mainly of ethnic Poles and Hungarians, who live predominantly in the western regions of the country.
Protestant Christians also form around 2.19 percent of the population. Protestant numbers have grown greatly since Ukrainian independence. The Evangelical Baptist Union of Ukraine is the largest group, with more than 150,000 members and about 3000 clergy. The second largest Protestant church is the Ukrainian Church of Evangelical faith (Pentecostals) with 110000 members and over 1500 local churches and over 2000 clergy, but there also exist other Pentecostal groups and unions and together all Pentecostals are over 300,000, with over 3000 local churches. Also there are many Pentecostal high education schools such as the Lviv Theological Seminary and the Kiev Bible Institute. Other groups include Calvinists, Jehovah's Witnesses, Lutherans, Methodists and Seventh-day Adventists. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormon Church) is also present.
There are an estimated 500,000 Muslims in Ukraine, and about 300,000 of them are Crimean Tatars. There are 487 registered Muslim communities, 368 of them on the Crimean peninsula. In addition, some 50,000 Muslims live in Kiev; mostly foreign-born. The Jewish community is a tiny fraction of what it was before World War II. The cities with the largest populations of Jews in 1926 were Odessa, 154,000 or 36.5% of the total population; and Kiev, 140,500 or 27.3%.The 2001 census indicated that there are 103,600 Jews in Ukraine, although community leaders claimed that the population could be as large as 300,000. There are no statistics on what share of the Ukrainian Jews are observant, but Orthodox Judaism has the strongest presence in Ukraine. Smaller Reform and Conservative Jewish (Masorti) communities exist as well.
Education
According to the Ukrainian constitution, access to free education is granted to all citizens. Complete general secondary education is compulsory in the state schools which constitute the overwhelming majority. Free higher education in state and communal educational establishments is provided on a competitive basis. There is also a small number of accredited private secondary and higher education institutions.
Due to the Soviet Union's emphasis on total access of education for all citizens, which continues today, the literacy rate is an estimated 99.4 percent. Since 2005, an eleven-year school program has been replaced with a twelve-year one: primary education takes four years to complete (starting at age six), middle education (secondary) takes five years to complete; upper secondary then takes three years. In the 12th grade, students take Government Tests, which are also referred to as school-leaving exams. These tests are later used for university admissions.
The Ukrainian higher education system comprises higher educational establishments, scientific and methodological facilities under federal, municipal and self-governing bodies in charge of education. The organisation of higher education in Ukraine is built up in accordance with the structure of education of the world's higher developed countries, as is defined by UNESCO and the UN.
Infrastructure
Most of the Ukrainian road system has not been upgraded since the Soviet era, and is now outdated. The Ukrainian government has pledged to build some 4,500 km (2,800 mi) of motorways by 2012. In total, Ukrainian paved roads stretch for 164,732 kilometres (102,360 mi).
Rail transport in Ukraine plays the role of connecting all major urban areas, port facilities and industrial centers with neighbouring countries. The heaviest concentration of railroad track is located in the Donbas region of Ukraine. Although the amount of freight transported by rail fell by 7.4 percent in 1995 in comparison with 1994, Ukraine is still one of the world's highest rail users. The total amount of railroad track in Ukraine extends for 22,473 kilometres (13,964 mi), of which 9,250 kilometres (5,750 mi) is electrified.
Ukraine is one of Europe’s largest energy consumers; it consumes almost double the energy of Germany, per unit of GDP. A great share of energy supply in Ukraine comes from nuclear power, with the country receiving most of its nuclear fuel from Russia. The remaining oil and gas, is also imported from the former Soviet Union. Ukraine is heavily dependent on its nuclear energy. The largest nuclear power plant in Europe, the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Plant, is located in Ukraine. In 2006, the government planned to build 11 new reactors by the year 2030, in effect, almost doubling the current amount of nuclear power capacity. Ukraine's power sector is the twelfth-largest in the world in terms of installed capacity, with 54 gigawatts (GW). Renewable energy still plays a very modest role in electrical output, and in 2005 energy production was met by the following sources: nuclear (47 percent), thermal (45 percent), hydro and other (8 percent).
Wikipedia
Ukraine for You